pg_rewind 代码浅析
pg_rewind 是 Postgres 9.5 引入的用于将旧主库上的状态回退到与新主库一个共同的历史点上,进而可以将旧主库作为 standby 与新主库构成主备以提供高可用。对于数据量较大且写入不是很频繁的数据库实例,pg_rewind 相较于 pg_basebackup 在恢复时间上有优势。
注: 本文分析基于源码 Postgres 16devel (commit 3f58a4e2960a9509036b7d94beab64a747dc59dc)
执行 pg_rewind 需要满足以下条件:
the target server either has the
wal_log_hintsoption enabled in postgresql.conf or data checksums enabled when the cluster was initialized with initdb. Neither of these are currently on by default.
full_page_writesmust also be set to on, but is enabled by default.
使用方式:
pg_rewind --target-pgdata=db-master --source-server="port=5432 user=postgres dbname=postgres" --progress
不同于 pg_basebackup 需要 server 端使 walsender 处理客户端特殊的消息,pg_rewind 使用普通的 SQL 语句就可完成其需要的功能,因此没有相关的 server 端代码。其代码在 src/bin/pg_rewind 目录下:
datapagemap.c -- A data structure for keeping track of data pages that have changed
file_ops.c -- helper functions for writing to the target data directory
filemap.c -- contains the logic to decide what to do with different kinds of files, and the data structure to support it
libpq_source.c -- Functions for fetching files from a remote server via libpq
local_source.c -- Functions for using a local data directory as the source
parsexlog.c -- Functions for reading Write-Ahead-Log
pg_rewind.c -- pg_rewind 主函数逻辑
timeline.c -- timeline-related functions
xlogreader.c -- Generic XLog reading facility
pg_rewind 主流程
pg_rewind 作为一个标准的客户端程序,与 server 的交互使用 SQL 语句完成,因此逻辑相对简单。其整体流程如下图所示:
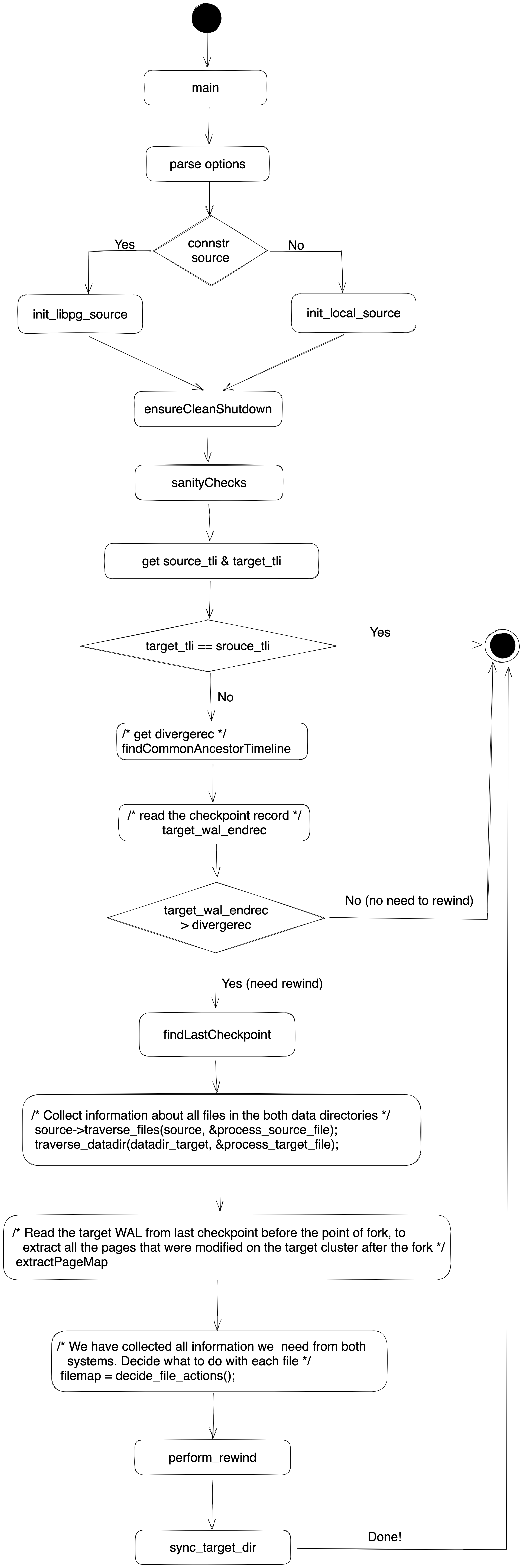
我们看几个比较重要的函数:
init_libpq_source
/*
* Create a new libpq source.
*
* The caller has already established the connection, but should not try
* to use it while the source is active.
*/
rewind_source *
init_libpq_source(PGconn *conn)
{
libpq_source *src;
init_libpq_conn(conn);
src = pg_malloc0(sizeof(libpq_source));
src->common.traverse_files = libpq_traverse_files;
src->common.fetch_file = libpq_fetch_file;
src->common.queue_fetch_file = libpq_queue_fetch_file;
src->common.queue_fetch_range = libpq_queue_fetch_range;
src->common.finish_fetch = libpq_finish_fetch;
src->common.get_current_wal_insert_lsn = libpq_get_current_wal_insert_lsn;
src->common.destroy = libpq_destroy;
src->conn = conn;
initStringInfo(&src->paths);
initStringInfo(&src->offsets);
initStringInfo(&src->lengths);
return &src->common;
}
因为有两种 source,libpg source 和 local source,pg_rewind 将这块进行了抽象,如上初始化对相关 hook 进行了赋值。
findCommonAncestorTimeline
static void
findCommonAncestorTimeline(TimeLineHistoryEntry *a_history, int a_nentries,
TimeLineHistoryEntry *b_history, int b_nentries,
XLogRecPtr *recptr, int *tliIndex)
{
int i,
n;
/*
* Trace the history forward, until we hit the timeline diverge. It may
* still be possible that the source and target nodes used the same
* timeline number in their history but with different start position
* depending on the history files that each node has fetched in previous
* recovery processes. Hence check the start position of the new timeline
* as well and move down by one extra timeline entry if they do not match.
*/
n = Min(a_nentries, b_nentries);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a_history[i].tli != b_history[i].tli ||
a_history[i].begin != b_history[i].begin)
break;
}
if (i > 0)
{
i--;
*recptr = MinXLogRecPtr(a_history[i].end, b_history[i].end);
*tliIndex = i;
return;
}
else
{
pg_fatal("could not find common ancestor of the source and target cluster's timelines");
}
}
如上函数通过解析源端和目的端的 timeline history 文件找到其分叉的 timeline 及 分叉 LSN。
findLastCheckpoint 读取 wal 找到分叉点之前的 checkpoint。
/*
* Find the previous checkpoint preceding given WAL location.
*/
void
findLastCheckpoint(const char *datadir, XLogRecPtr forkptr, int tliIndex,
XLogRecPtr *lastchkptrec, TimeLineID *lastchkpttli,
XLogRecPtr *lastchkptredo, const char *restoreCommand)
{
/* Walk backwards, starting from the given record */
XLogRecord *record;
XLogRecPtr searchptr;
XLogReaderState *xlogreader;
char *errormsg;
XLogPageReadPrivate private;
/*
* The given fork pointer points to the end of the last common record,
* which is not necessarily the beginning of the next record, if the
* previous record happens to end at a page boundary. Skip over the page
* header in that case to find the next record.
*/
if (forkptr % XLOG_BLCKSZ == 0)
{
if (XLogSegmentOffset(forkptr, WalSegSz) == 0)
forkptr += SizeOfXLogLongPHD;
else
forkptr += SizeOfXLogShortPHD;
}
private.tliIndex = tliIndex;
private.restoreCommand = restoreCommand;
xlogreader = XLogReaderAllocate(WalSegSz, datadir,
XL_ROUTINE(.page_read = &SimpleXLogPageRead),
&private);
if (xlogreader == NULL)
pg_fatal("out of memory while allocating a WAL reading processor");
searchptr = forkptr;
for (;;)
{
uint8 info;
XLogBeginRead(xlogreader, searchptr);
record = XLogReadRecord(xlogreader, &errormsg);
if (record == NULL)
{
if (errormsg)
pg_fatal("could not find previous WAL record at %X/%X: %s",
LSN_FORMAT_ARGS(searchptr),
errormsg);
else
pg_fatal("could not find previous WAL record at %X/%X",
LSN_FORMAT_ARGS(searchptr));
}
/*
* Check if it is a checkpoint record. This checkpoint record needs to
* be the latest checkpoint before WAL forked and not the checkpoint
* where the primary has been stopped to be rewound.
*/
info = XLogRecGetInfo(xlogreader) & ~XLR_INFO_MASK;
if (searchptr < forkptr &&
XLogRecGetRmid(xlogreader) == RM_XLOG_ID &&
(info == XLOG_CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN ||
info == XLOG_CHECKPOINT_ONLINE))
{
CheckPoint checkPoint;
memcpy(&checkPoint, XLogRecGetData(xlogreader), sizeof(CheckPoint));
*lastchkptrec = searchptr;
*lastchkpttli = checkPoint.ThisTimeLineID;
*lastchkptredo = checkPoint.redo;
break;
}
/* Walk backwards to previous record. */
searchptr = record->xl_prev;
}
XLogReaderFree(xlogreader);
if (xlogreadfd != -1)
{
close(xlogreadfd);
xlogreadfd = -1;
}
}
libpq_traverse_files 通过 SQL 语句遍历查询源端的文件。
/*
* Get a list of all files in the data directory.
*/
static void
libpq_traverse_files(rewind_source *source, process_file_callback_t callback)
{
PGconn *conn = ((libpq_source *) source)->conn;
PGresult *res;
const char *sql;
int i;
/*
* Create a recursive directory listing of the whole data directory.
*
* The WITH RECURSIVE part does most of the work. The second part gets the
* targets of the symlinks in pg_tblspc directory.
*
* XXX: There is no backend function to get a symbolic link's target in
* general, so if the admin has put any custom symbolic links in the data
* directory, they won't be copied correctly.
*/
sql =
"WITH RECURSIVE files (path, filename, size, isdir) AS (\n"
" SELECT '' AS path, filename, size, isdir FROM\n"
" (SELECT pg_ls_dir('.', true, false) AS filename) AS fn,\n"
" pg_stat_file(fn.filename, true) AS this\n"
" UNION ALL\n"
" SELECT parent.path || parent.filename || '/' AS path,\n"
" fn, this.size, this.isdir\n"
" FROM files AS parent,\n"
" pg_ls_dir(parent.path || parent.filename, true, false) AS fn,\n"
" pg_stat_file(parent.path || parent.filename || '/' || fn, true) AS this\n"
" WHERE parent.isdir = 't'\n"
")\n"
"SELECT path || filename, size, isdir,\n"
" pg_tablespace_location(pg_tablespace.oid) AS link_target\n"
"FROM files\n"
"LEFT OUTER JOIN pg_tablespace ON files.path = 'pg_tblspc/'\n"
" AND oid::text = files.filename\n";
res = PQexec(conn, sql);
if (PQresultStatus(res) != PGRES_TUPLES_OK)
pg_fatal("could not fetch file list: %s",
PQresultErrorMessage(res));
/* sanity check the result set */
if (PQnfields(res) != 4)
pg_fatal("unexpected result set while fetching file list");
/* Read result to local variables */
for (i = 0; i < PQntuples(res); i++)
{
char *path;
int64 filesize;
bool isdir;
char *link_target;
file_type_t type;
if (PQgetisnull(res, i, 1))
{
/*
* The file was removed from the server while the query was
* running. Ignore it.
*/
continue;
}
path = PQgetvalue(res, i, 0);
filesize = atol(PQgetvalue(res, i, 1));
isdir = (strcmp(PQgetvalue(res, i, 2), "t") == 0);
link_target = PQgetvalue(res, i, 3);
if (link_target[0])
type = FILE_TYPE_SYMLINK;
else if (isdir)
type = FILE_TYPE_DIRECTORY;
else
type = FILE_TYPE_REGULAR;
process_source_file(path, type, filesize, link_target);
}
PQclear(res);
}
process_source_file 和 process_target_file 将源端和目的端读取的文件保存到 filehash 这个全局变量中,extractPageMap 通过读取分叉点之前 checkpoint 到 target_wal_endrec 之间的 WAL 来获取修改的文件块,更新到 file_entry 的 bitmap 中。
当收集完源端和目的端的文件信息后,调用 decide_file_actions 来决定对每个文件做何种操作,包括:
- FILE_ACTION_CREATE /* create local directory or symbolic link */
- FILE_ACTION_COPY /* copy whole file, overwriting if exists */
- FILE_ACTION_COPY_TAIL /* copy tail from 'source_size' to 'target_size' */
- FILE_ACTION_NONE /* no action (we might still copy modified blocks based on the parsed WAL) */
- FILE_ACTION_TRUNCATE /* truncate local file to 'newsize' bytes */
- FILE_ACTION_REMOVE /* remove local file / directory / symlink */
perform_rewind 根据 filemap 对目标端中的每个文件作相应的操作,并创建一个 backup_label 文件用于强制从上一个共同的 checkpoint 开始恢复,最后更新 controlfile。运行 pg_rewind 之后,实例启动是通过回放 wal 日志来保证数据的一致性,即当 target 实例启动后,进程进入 DB_IN_ARCHIVE_RECOVERY 模式,从分叉点前的第一个 checkpoint 回放源端生成的 wal 日志。
Ref 2 对 pg_rewind 的原理进行了详细的介绍。