捍卫代码质量 —— git 篇
我之前有篇文章讲了 git 的各种命令,是为了在需要的时候方便查看。本篇我想从实际的工作场景出发,来看看如何通过更合理地使用 git,来提高我们的工作效率以及代码质量。
About Git
- VCS — cvs/svn/mercurial
- Linus Torvalds
- Github/Gitlab
Git 的三个重要概念
1. Snapshots, Not Differences
不同于其他 VCS,git 并不是将文件的差异作为数据来存储, 而是将每一次 commit 看做一个快照,当获取一个文件在不同版本之间的差异时,是将两个版本之间的快照进行比对。我们可以将 git 看作一个支持快照的迷你文件系统。
Not this
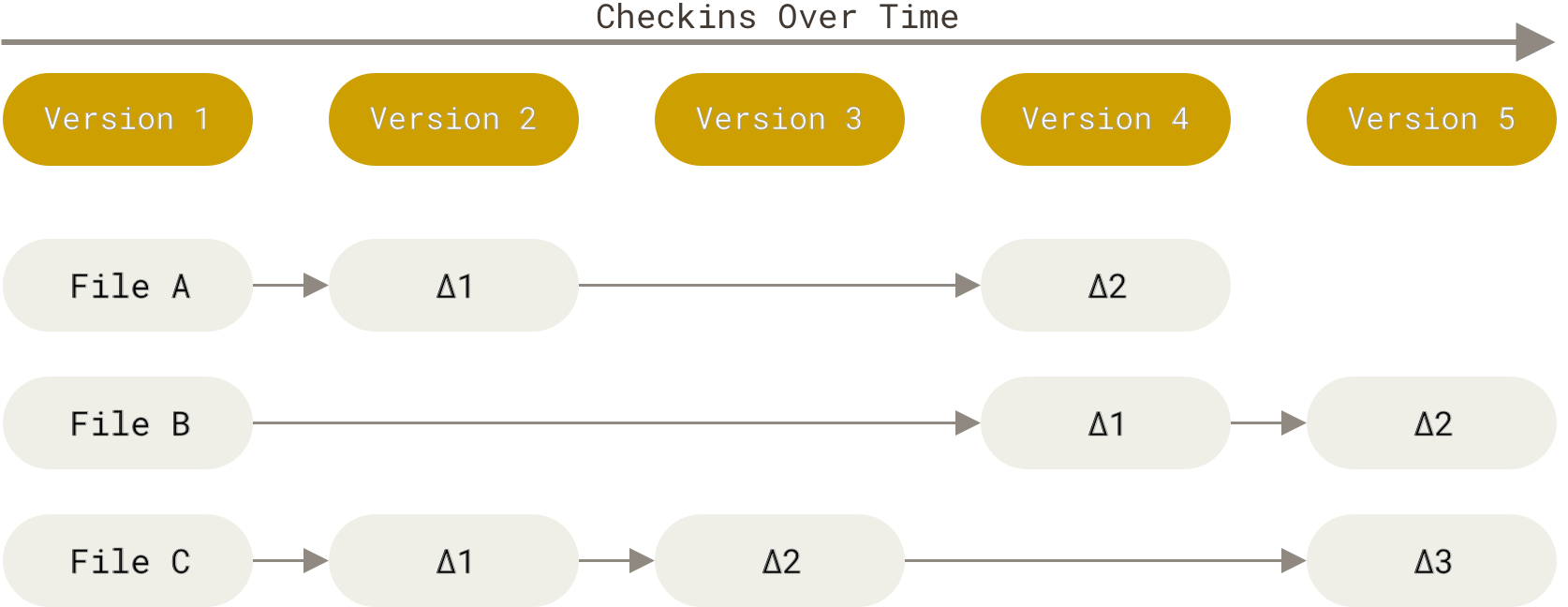
But this
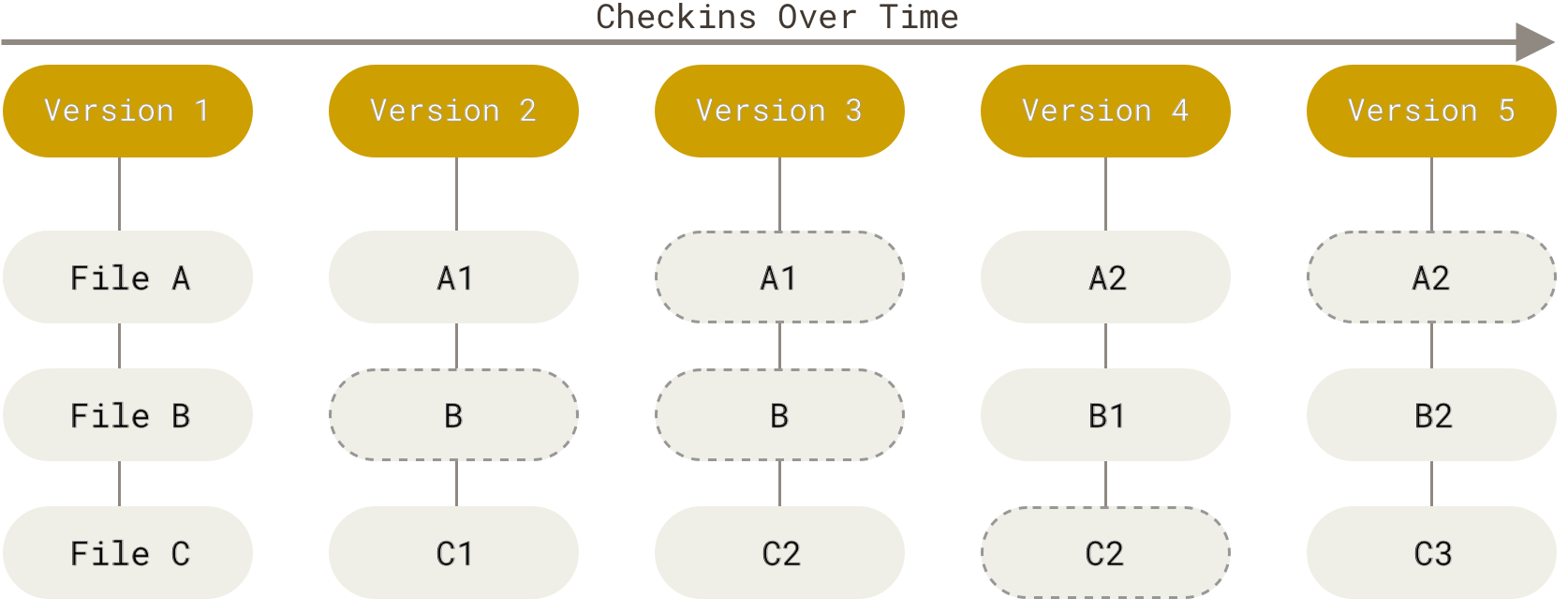
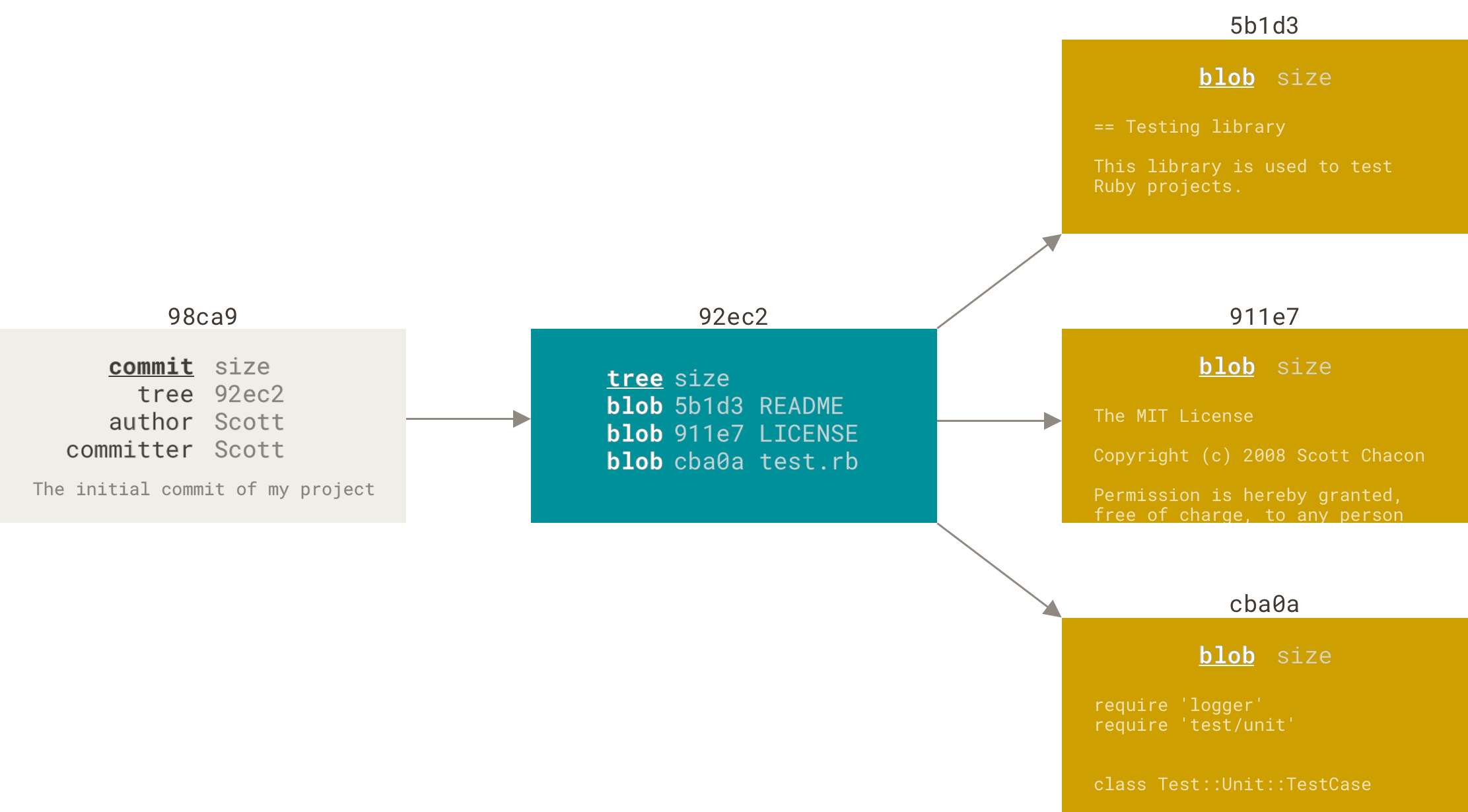
每个 commit 对应某一时刻 git 文件系统的快照,而 blog 则为某一文件特定时刻的快照。
2. Three States
Git 中几乎所有操作都是在本地完成,然后再与远端仓库同步,这使得 Git 可以在没有网络的情况下使用。
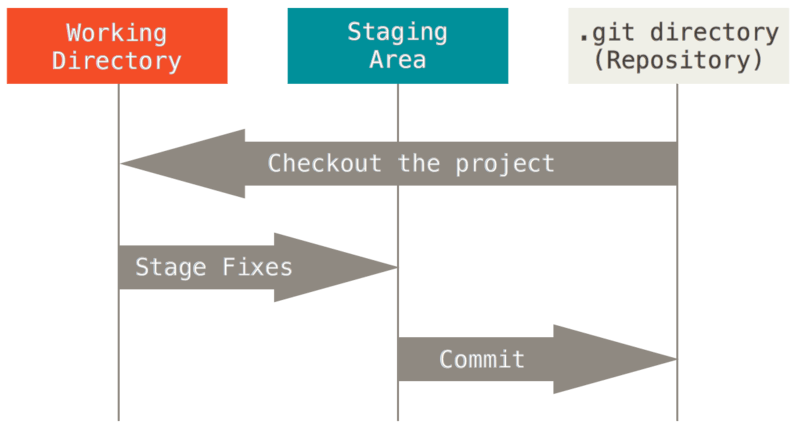
Git 本地由三个部分组成,官方解释如下:
The working tree is a single checkout of one version of the project. These files are pulled out of the compressed database in the Git directory and placed on disk for you to use or modify.
The staging area is a file, generally contained in your Git directory, that stores information about what will go into your next commit. Its technical name in Git parlance is the “index”, but the phrase “staging area” works just as well.
The Git directory is where Git stores the metadata and object database for your project.
用大白话解释:
- 工作区(Working Directory):是项目的一个版本,它所显示的文件由 .git 目录中的数据生成并存放到本地供用户使用或修改。
- 实验1 - 从 .git 目录恢复工作区
- 暂存区(Staging Area):是一个二进制文件
.git/index,保存了按文件路径排序的文件列表,git ls-files --stage可以查看其内容,其中 SHA1 值对应文件的 blob 对象。将一个文件从工作区add到暂存区主要体现在对该文件的修改。[root@centos hadoop]# git ls-files --stage | head -n5 100644 33aa676715cb184101bf71f579453c6587b91dfc 0 .gitattributes 100644 2b5014b7b234d3ce846d9dd22826cc0c3142df18 0 .github/pull_request_template.md 100644 551b1b5361ce2519e616fb00bc4101ad51e5f57e 0 .gitignore 100644 6f33a60f41103b3c07055062e45e8de0b2bfe7a7 0 BUILDING.txt 100644 11cbb9189cfba4339fa0e8fea95e364ff29d8d39 0 Jenkinsfile- 实验2 - 修改一个文件,查看其加到暂存区前后不同的 blog 对象内容
- .git 目录:Git 保存元数据和对象数据路的地方。
- 实验3 - 承接实验2,查看 commit 前后 index 文件及 refs/heads/master 的变化
Git 管理的文件在三种状态之间变换:Modified 表示修改过但还未添加到暂存区的文件,Staged 表示修改过且已经添加到暂存区的文件,Committed 表示这个文件被安全保存到了 Git 仓库。当然,新增的文件由于还未被 git 接管,其状态为 Untracked。
因此 Git 的基本工作流程可以总结如下:
- 修改工作区中的文件
- 选择性地将你想要提交到下一个commit的改动标记为 Stage 状态,既放到暂存区
- 提交,将暂存区的文件存储到本地Git仓库
3. Branch
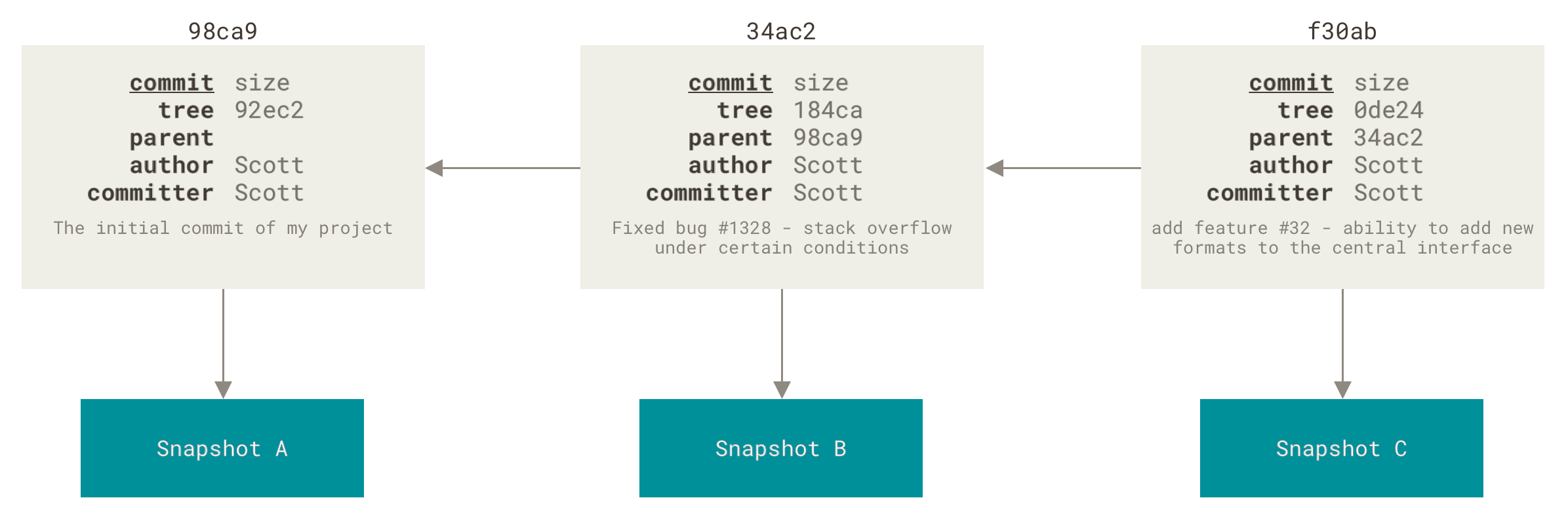
Git 的分支模型是它的 “Killer feature”,因为对于其它VCS,分支可能意味着一份新的源码拷贝,这是一个昂贵的操作,而 Git 的分支模型非常轻量。得益于快照的概念,我们可以把分支看做一个指向某个快照版本的指针,切换分支就像是指针在不同的快照上移动。
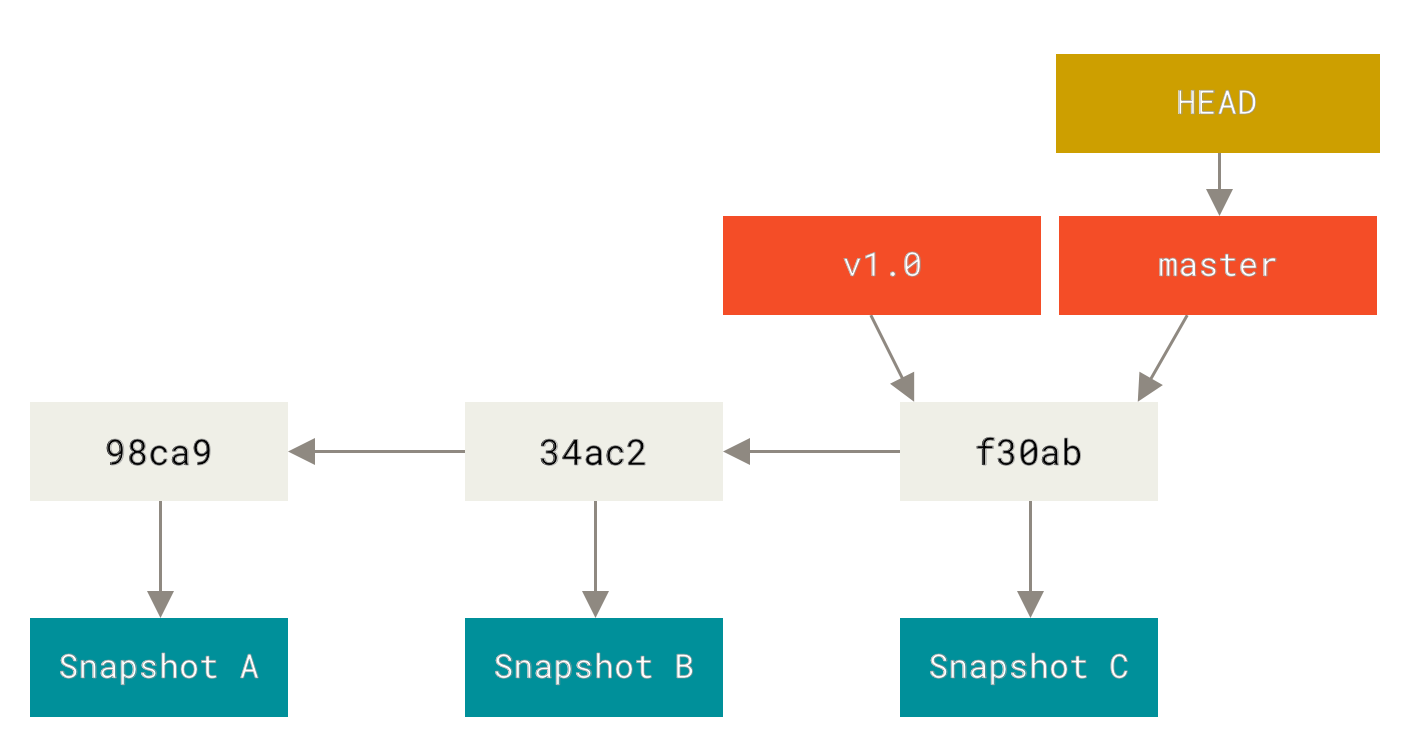
不同场景如何合理地使用 Git
下面从几个实际的工作场景出发,来看看我们应该如何合理地使用 git。
场景1. 新入职
刚入职的同事申请了代码仓库权限之后,会从远端的代码仓库 clone 一份到本地,然后根据一些指导手册配置一下 Git,主要包含两点:
a) config 配置用于在 commit 的时候将程序员信息记到 log 里
# global 的配置是将配置项添加到了 ~/.gitconfig 或 ~/.config/git/config
# --system 和 --local 的配置参考 https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-First-Time-Git-Setup
git config --global user.email zhjwpku@gmail.com
git config --global user.name "Zhao Junwang"
git config --global core.editor vim
b) SSH keys 配置用于远程仓库的认证
# 该命令用于生成一组对称秘钥
ssh-keygen
# 将如下公钥添加到 CodeClub 的个人 Setting 对应的 SSH Key 管理页面中
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAACAQCquijUKukfBTWYF9X9m/01CzC1Zhi3hDg9KCtcDqXAwYb9R2cGMjq6co3iro8Ezn7oN3mM5SFoFMj5PovIlw/UerOcf9KL4Q3xjbiwxAmftO4g5LYUrpFQdR+OQA8p3gEpFd16doO4Hxfdb3/EHjlHXtjdXXe43oUS9ax++3ufbenZ6mlqEKiWP1SBXXY4D4gGcOFef+RHj2T04eoB7aH1LmICumOAad0OwHzLOCm4gvyC2Rl5AV3iURYFTdBwVaSD0vVvhx4UH5W8XcHRmO9ejuGHhfgvZ6Aroj7EKnl+WEhKuNnw3LV2TqrJELZA8bTWMBFVKyOp78BsZb47U+wT8Wzx2RphEpnPIk7ucR1endXPV8P/PnyVWP92rQy56Ud+9VGlFqvU8N1Ky8RK7Q94XDCGD0o2YTm5B8at2DQ+Ka3bLc7n0fcnPAnuyQXVeQSvXvwiKmKdIt1c4k+8pfBrYUHFpLpac0Gin88Ck0DSu7X+Bb+IY3d6hzLiIdFpZ0wPWqpF45MArJC6zuph0Z2QYMHvhfHlkxv2VCcM8d+tdT8rJWcs9aG8DQVRvGeHstkibrUrbNIFCkJsb2jXoPN0qTpv0p51PNKidkQxa14/a0LkkccbSQLp21iLpspQO0/HVFi9mZIpZgTHGP5omNsi+s/VPZH1tDcUMrZ7pXyTGw== zhjwpku@gmail.com
完成上面两个配置之后,就可以开始写代码了。
场景2. 正常工作流程
我们使用 git 的方式属于 Feature Branch Workflow,基本上都是基于 master 拉分支,然后开发自测,提交代码,push 分支,然后再网页上提 Merge Request,门禁跑过,commmitter review 通过,就可以被 Merge 了,假设这一套流程非常顺利,那么在本地仓库需要用到的 git 命令大致如下:
首先要有一个干净的与远端仓库一致的 master 分支
# 方法 1
git fetch origin // 将远端仓库的变动同步到 .git 目录,但不对工作目录做任何修改,本地的 master 并不是最新的
# 方法 2
git checkout master // 切到 master 分支
git pull // git fetch origin && git merge origin/master,本地 master 是最新的
切分支
# 方法 1.1 假如当前处于 master 分支且 master 分支为最新
git branch your_feature_branch
git checkout your_feature_branch
# 方法 1.2 等同于上面两个命令
git checkout -b your_feature_branch
# 方法 2 无论当前处于哪个分支,只要 origin/master 是最新的
git checkout -b your_feature_branch origin/master
提交代码
# 将需要提交的改动添加到暂存区,git status 会提示应该用哪些命令来实现
git add added_or_changed_file
git add added_or_changed_dir
git rm deleted_file
git rm -r deleted_dir
# 提交到本地仓库,-s => Signed-off-by,有些开源社区要求,可选
git commit -s -m "short message"
git commit -s // 在 vim 编辑器里详细描述该 commit 做了哪些修改
注:不建议使用 git add . 和 git commit -a
push 分支
git push origin your_feature_branch
场景3. 开发自验没通过,需要进行修改
有些程序员可能不习惯使用 beyond compare 来同步本地和编译机的代码(比如我更信任 git 的 commit id),那想要在本地(编辑)、CodeClub(Center Repo)、Ubuntu(编译验证)三个仓库上同步代码,一般的做法是将本地分支 push 到 CodeClub,然后在编译机上将分支从 CodeClub pull 下来,再编译验证。
注:可以通过 git remote add 命令将编译环境的 git 仓库作为远端仓库添加到本地 config,然后将本地的分支 push 到该仓库,见场景 14
如果编译验证不通过,本地就会存在一个不可编译的 commit。一些对代码管理较严格的开源社区,会要求所有的 commit 是可编译的,这对后期使用 git bisect 定位问题更加友好。git commit --amend可以将后来的修改与前一个 commit 合并到一起。
The git commit --amend command is a convenient way to modify the most recent commit. It lets you combine staged changes with the previous commit instead of creating an entirely new commit.
实验4 - 演示 git commit –amend
场景4. 将已存在的多个 commit 合为一个
在开发一个比较棘手的特性时,改一点提一点验一下,因为每次改动可能并没有实际的意义,因此会使用之前的 commit message 作为本次的 commit message,这就会造成分支上有很多相同类型的 commit,这时候 git commit --amend 就解决不了这个问题了,git reset 可以很方便地解决这个问题。
实验5 - 演示 git reset
# init git repo
mkdir test_git_reset && cd test_git_reset && git init
echo "Hello world Init" >> helloworld.txt && git add helloworld.txt && git commit -s -m "Hello world Init"
git checkout -b test_git_rest
for i in {1..20}
do
echo "Hello world $i" >> helloworld.txt &&
git add helloworld.txt &&
git commit -s -m "Hello world $i"
done
注:上面的操作会使得本地分支跟远端仓库的同名分支呈非线性结构,需要用 git push origin your_feautre_branch -f 来强推
场景5. 提交MR页面报 Conflict
几乎每个程序员都会遇到合并冲突。对于这种问题我现在知道的有三种方法。
a) 在页面上解决
CodeClub 将用户的 RESTful 请求转化成 git 命令,相当于代替用户手动操作了,不推荐,因为我不会 🙈。
b) git merge
先将 master merge 到特性分支上,有冲突则解决冲突,然后将分支强推到远端。
- 所有的 commit id 都保留
- 只需要解决一次(但在差异很大的情况下,解决起来相对更困难)
- 解决完冲突用 git commit 添加一个解决冲突的 commit
- 放弃本次 merge 用 git merge –abort
c) git rebase
在 master 的基础上将特性分支的每一个 commit 重新提交,在这个过程中解决冲突,然后将分支强推到远端。
- 特性分支的所有 commit id 都变了,因为是新的 commit
- 过程中 git add 和 git rebase –continue 解决每一个 commit 修改
- 有些 commit 可能在之前的 commit 中已经修改,这次 commit 可能就没有任何改动,使用 git rebase –skip 将该 commit 忽略
- 放弃本次 rebase 用 git rebase –abort
实验6 - 演示 merge 跟 rebase 的不同
mkdir test_git_merge_and_rebase && cd test_git_merge_and_rebase && git init
echo "Hello world Init" >> helloworld.txt && git add helloworld.txt && git commit -s -m "Hello world Init"
git checkout -b test_git_rest
for i in {1..10}
do
echo "Hello world $i" >> helloworld.txt &&
git add helloworld.txt &&
git commit -s -m "Hello world $i"
git checkout -
done
注:git checkout - 用于切到之前工作的分支
rebase 最终的结果所有的 commit 呈现线性关系,在每次解决冲突的时候能够明确知道每一个 commit 做了哪些改动,有助于重新理解代码,推荐使用 rebase。
注:对于一个大特性的开发,可能经常需要 rebase master,为了减少解决冲突的工作,git-rerere 也许能帮到你
实验7 - 用 git rebase 解决场景4的问题
场景6. 主线上改了个BUG
在特性分支的开发过程中,主线可能已经合入了很多其它的特性,其中包括一个跟本特性相关的 bug-fix,需要把它同步到特性分支支撑测试。当只需要其中有限几个 commit 的时候就需要用到 git cherry-pick。
git cherry-pick <commit_id>
场景7. 正在开发一个特性的时候,PL让我去修一个已定位的紧急 bug
本地特性没有开发完,又要从 master 切一个分支去修 bug,两种方法。
a) 提交到本地
git add modified_file
git commit -s -m "Unfinished commit"
git fetch origin
git checkout -b bug-fix origin/master
# 修改并提交之后
git checkout -
# 继续之前特性的开发
git commit --amend
b) stash
git stash
git fetch origin
git checkout -b bug-fix origin/master
# 修改并提交之后
git checkout -
git stash pop
场景8. 这段代码我看不懂
当有代码看不懂的时候,急切想要找到代码的作者请教一下,git blame 可以查看每一行代码对应的作者和 commit id,根据 commit id 还能查看所有的改动和对应时刻的文件内容。
git blame filename.txt
# 查看这个 commit_id 做了哪些改动
git show <commit_id>
# 查看对应 commit_id 的时候那个文件是什么样的
git show <commit_id>:filename.txt
# 查看这个 commit 提交之前 filename.txt 是什么样的
git show <commit_id>~:filename.txt
# 查看这个 commit_id 改了哪些文件
git show --name-only <commitid>
注:在修改目录结构的时候,如果代码不是自己写的,最好在函数头上把原作者信息加上
实验8 - 演示 git blame 和 git show
场景9. 我知道一个 commit_id,但这是哪个分支上的代码?
git branch --contains <commit_id>
git branch -r --contains <commit_id>
git branch -a --contains <commit_id>
场景10. 我的编译机上好多临时文件,拉代码老报错
git clean -dfx
git reset --hard HEAD
场景11. 我想查看主线上这个文件最新是什么样的
# 路径要写全
git show master:the_file_you_want_to_see
场景12. 删除老旧分支
用 git branch 看了一下,好多分支应该都已经合到主线了,应该可以删了。
# 查看有没有合到主线
git log branch_name // 查看该分支的最新 commit_id
git branch -r --contains <commit_id> | grep master
git branch --merged // 在 master 分支上执行该命令也能查看 merge 到 master 的分支
# 删除本地分支
git branch -d branch_name
# 删除远端分支,可以在界面上操作,也可以用如下命令
git push --delete origin branch_name
git push origin :branch_name
场景13. 查看暂存区做了哪些修改
git diff 的用法也千奇百怪。
# 比较工作目录和暂存区的差异
git diff
git diff --name-only // 只显示不同的文件名
# 比较暂存区和前一个版本时间的差异
git diff --cached
# 显示一个文件在不同分支有什么不同
git diff mybranch master -- filename
场景14. 每次都要经过中心仓库同步本地跟编译机的代码,很烦
可以使用 git remote add 直接将编译机的仓库设置为本地仓库的远程仓库。
实验9 - 演示 git remote add
git remote add ubuntu /path/to/git/repo
git config --bool core.bare true
场景15. git bisect
git bisect start
git bisect bad # Current version is bad
git bisect good v2.6.13-rc2 # v2.6.13-rc2 is known to be good
与项目管理相关的命令
git 还有些命令与项目管理息息相关。
# 用于解决项目依赖关系
git submodule
# 用于包管理工具
git tag -a 1.0.0 -m "Release 1.0.0"
git describe
快捷命令
git 可以设置命令别名,根据个人习惯设置,推荐几个与 git log 相关的。
git config --global alias.lg "log --graph --format='%C(auto)%h%C(reset) %C(dim white)%an%C(reset) %C(green)%ai%C(reset) %C(auto)%d%C(reset)%n %s'"
git config --global alias.lg10 "log --graph --pretty=format:'%C(yellow)%h%C(auto)%d%Creset %s %C(white)- %an, %ar%Creset' -10"
git config --global alias.lg20 "log --graph --pretty=format:'%C(yellow)%h%C(auto)%d%Creset %s %C(white)- %an, %ar%Creset' -20"
git config --global alias.lg30 "log --graph --pretty=format:'%C(yellow)%h%C(auto)%d%Creset %s %C(white)- %an, %ar%Creset' -30"
.gitignore
这个我们的工程里现在没有,要加。
# Object files
*.o
*.ko
*.obj
*.elf
# Linker output
*.ilk
*.map
*.exp
# Precompiled Headers
*.gch
*.pch
# Libraries
*.lib
*.a
*.la
*.lo
# Shared objects
*.so
*.so.*
对应的视频讲解