MySQL实用技巧
笔者对 MySQL 从来心存敬畏,一直期望成为一名懂一丢丢 DBA 的研发😏,在此记录开发中与 MySQL 相关的点滴。
1. 字段中带空格的值的查询方法
有这样一组数据(通过 select * from user where nickName like "%marz%"; 获取):
| id | age | sex | nickName |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 0 | marzxwell |
| 2 | 30 | 0 | Marzuki Manuel |
| 3 | 40 | 1 | Marz Kimz |
| 4 | 50 | 1 | Marzuqah Amuni |
现在有一个需求,当查询条件为 MarzukiManuel 或 Marzuki Manuel 都要求把第二条数据查出。由于内容的不确定,需要一种通用的查询方式:
select * from user where trim(replace(nickName,' ','')) like trim(replace('%Marzuki Manuel%',' ',''));
select * from user where trim(replace(nickName,' ','')) like trim(replace('%MarzukiManuel%',' ',''));
如此不论传进来的值中是否带有空格,都能够获取所需的结果。
2. 高效同步 MySQL 表数据
pt-table-sync 是 Percona Toolkit 命令集中用于高效同步 MySQL 表数据的命令, 它常用于解决主从数据库之间的数据不一致。
安装
笔者使用的Ubuntu 16.04已经包含了Percona的软件源,直接apt-get install即可。
zhjwpku@ubuntu: ~ $ sudo apt-get install -y percona-toolkit
同步表数据
pt-table-sync的使用场景很多,笔者仅列出一种使用方法,不一定最优,但相对比较容易跟踪。
#!/bin/bash
DATA_DIR='/tmp'
DATE_SUFIX=`date +"%F-%H%M%S"`
DB_NAME=db1
TABLE_NAME=table1
SQL_FILE="$DATA_DIR/${DB_NAME}-${TABLE_NAME}-${DATE_SUFIX}.sql"
# host 192.168.1.11 与 192.168.1.10 的差异存入文件
pt-table-sync --print --verbose --charset=utf8 --databases $DB_NAME --tables $TABLE_NAME 'h=192.168.1.10,u=root,p=passwd' 'h=192.168.1.11,u=root,p=passwd' > $SQL_FILE
if [ -e $SQL_FILE ]
then
mysql -uroot -passwd -h192.168.1.11 $DB_NAME < $SQL_FILE
echo "db sync success"
exit 0
else
echo "$SQL_FILE not found"
exit 1
fi
3. dump 除默认表之外的所有表到一个文件中
#!/bin/bash
MYSQL_USERNAME=root
MYSQL_PASSWORD=rootpassword
MYSQL_HOST=10.0.63.6
MYSQL_CONN="-h${MYSQL_HOST} -u${MYSQL_USERNAME} -p${MYSQL_PASSWORD}"
EXCLUSIVE_DBS="'mysql', 'information_schema', 'performance_schema'"
#
# Collect all database names except for EXCLUSIVE_DBS
#
SQL="SELECT schema_name FROM information_schema.schemata WHERE schema_name NOT IN (${EXCLUSIVE_DBS})"
DBLIST=""
for DB in `mysql ${MYSQL_CONN} -ANe"${SQL}"` ; do DBLIST="${DBLIST} ${DB}" ; done
# --triggers option is enabled by default
# --routines 选项会把所有的存储过程和存储函数dump到sql文件
# --single-transaction 保证在备份的过程中得到一致性的备份
MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS="--routines --single-transaction"
mysqldump ${MYSQL_CONN} ${MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS} --databases ${DBLIST} > all-dbs.sql
注:mysqldump默认不会dump INFORMATION_SCHEMA和perfomance_schema 数据库
4. 批量更新某字段的顺序值
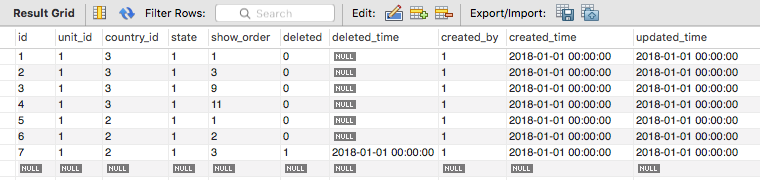
如图所示,将 unit_id = 1 且 country_id = 3 的所有行的 show_order 进行顺序值重排,即 (1, 3, 9, 11) -> (1, 2, 3, 4)。
1: 子查询
set @rownum = 0;
update ad_space s set s.show_order = (select @rownum := @rownum + 1 as nid)
where s.id in (select t.id from
(select ss.id from ad_space ss where ss.unit_id = 1 and
ss.country_id =3 and ss.state = 1 and ss.deleted = false
order by ss.show_order asc) t);
2: 表连接
set @rownum = 0;
update (select * from ad_space as ss where ss.unit_id = 1 and ss.country_id = 3 and
ss.state = 1 and ss.deleted = false order by ss.show_order asc) as t, ad_space s
set s.show_order = (select @rownum := @rownum + 1 as nid) where t.id = s.id;
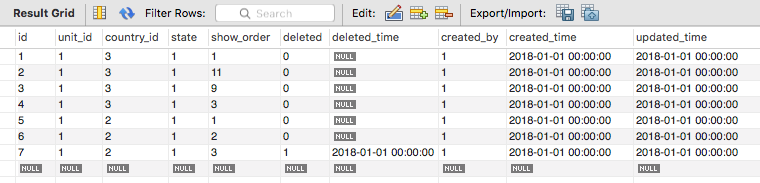
以上两条均能将上图中 (1, 3, 9, 11) 更新为 (1, 2, 3, 4),但对于下面的数据,想要将 (1, 11, 9, 3) 更新为 (1, 4, 3, 2),即保持 show_order 原有顺序,这两条语句就显得力不从心了,在此求教大拿指教。
注:如果执行过程中遇到 1175 错误,需执行 SET SQL_SAFE_UPDATES = 0; 或在 MySQL Workbench 偏好中进行设置(不勾选)。